Soybean sowing fertilizer law. Soybean growth is divided into seedling stage, branching stage, anthesis stage, crust stage, granule stage and maturity stage. The total growth period of 90 to 130 days, the law of fat absorption: the rate of nitrogen absorption. The emergence and branching period accounted for 15% of the total amount of nitrogen absorbed during the whole growth period, 16.4% from branching to full flowering, 28.3% from flowering to stalking, and 24% from drum bean. Flowering to grain size is the peak period of soybean nitrogen uptake. Phosphorus absorption rate. The seedling stage accounted for 17% of the initial flowering period, 70% of the early flowering period to the drum bean period, and 13% of the drum grain to the mature period. Phosphorus is needed most in the mid-growth stage of soybean. Absorption rate. Accumulative potassium absorption accounted for 43% before flowering, flowering to account for 39.5% of the granule phase, and still required to absorb 17.2% of potassium from drum grain to maturity. It can be seen that flowering to grain-filling period is the peak period of dry matter accumulation in soybean and the peak period of N, P, and K nutrients absorption. Soybean fertilization technical points. Soybean fertilization system is generally composed of basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer and topdressing fertilizer. The principle of fertilization is to ensure that soybeans have sufficient nutrition, but also to play a role in nitrogen fixation of rhizobia. Therefore, whether in the early or late growth stage, nitrogen should not be used in excess so as not to affect the growth of Rhizobium or cause lodging. On the other hand, it is also necessary to rectify the misconception that "there is no need for nitrogenous fertilizer for rhizobia." Fertilization should be done with a reasonable mix of N, P, K, trace elements such as boron and molybdenum, and combination of slow-acting and quick-acting fertilizers. Applying organic manure with basal fertilizer is the key measure for increasing soybean production. Organic fertilizers can be applied to the former crops on the crop rotation, while soybeans use their subsequent effects. It is conducive to nodulation and nitrogen fixation and increases soybean production. Soybeans can be grown on low-fertility soils and 10 kg of calcium phosphate and potassium chloride can be added as basal fertilizer, which is beneficial to soybean production. Fertilizers generally use 10 to 15 kilograms of superphosphate or 5 kilograms of diammonium phosphate per acre as a seed fertilizer, and boron-deficient soils add 0.4 to 0.6 kilograms of borax. Because soybeans are dicotyledonous crops, seedlings are difficult to top soil at the time of emergence. Seed dressings are best applied to the lower or lateral parts of seeds, and must not be in direct contact with fertilizers. Top dressing practice has proved that in the soybean seedling stage, when the root has not yet formed nodule, or when the nodule activity is weak, proper application of nitrogen fertilizer can make the plant grow robustly. It is also necessary to apply a small amount of nitrogen fertilizer at the flowering stage as appropriate. The amount of nitrogen fertilizer is generally 7.5 to 10 kg of urea applied. In addition, 0.2% to 0.3% potassium dihydrogen phosphate aqueous solution or superphosphate water spray at the flowering stage can increase the nitrogen content of the grain and have a significant effect on the yield; 0.1% borax, copper sulfate, and manganese sulfate are sprayed during the flowering period. Aqueous solution can promote full grain and increase soybean oil content.
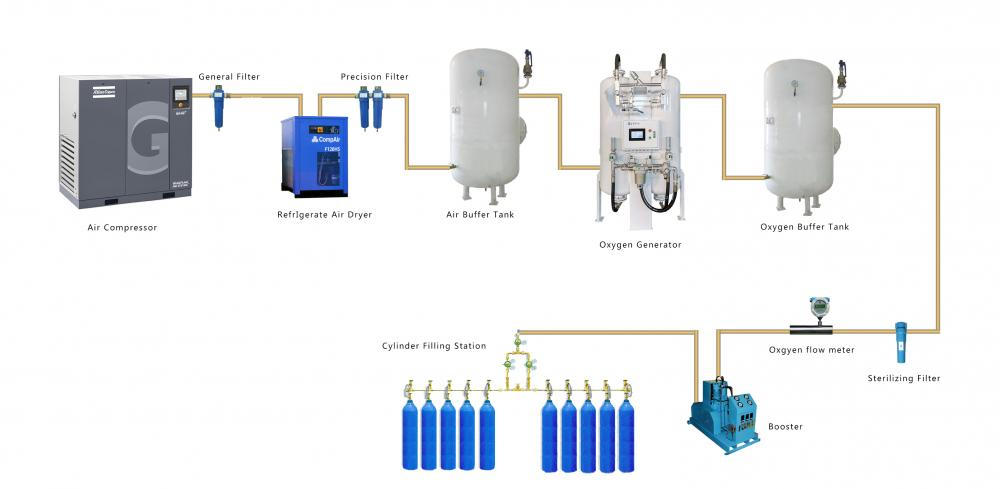
Oxygen Cylinder Filling System
With PSA principles, ETR Oxygen Cylinder Filling system can produce 93%±3% purity oxygen gas from compressed air directly. ETR oxygen cylinder filling system is consisted of Atlas screw air compressor, refrigerated air dryer, compressed air filter, air buffer tank, ETR Oxygen Plant, oxygen buffer tank, oxygen booster, cylinder filling station and HMI control cabinet.
Compressed air is purified through the air dryer and filters to a certain level for main plant to work with. Air buffer is incorporated for smooth supply of compressed air thus to reduce fluctuation of compressed air source. The plant produces oxygen with PSA (pressure swing adsorption) technology, which is a time proven oxygen generation method. Oxygen of desired purity at 93%±3% is delivered to oxygen buffer tank for smooth supply of product gas. Oxygen in buffer tank is maintained at 4bar pressure. With an oxygen booster, the oxygen pressure can be to 150bar and fill in cylinders.
Onsite Oxygen Cylinder Filling System Onsite Oxygen Cylinder Filling System,Oxygen Refilling System ,Oxygen Cylinder Filling,Oxygen Refilling Machine Hunan Eter Electronic Medical Project Stock Co., Ltd. , https://www.centralgas.be
Soybean fertilization technology
Soybean demand for major nutrients. Soybeans have relatively high economic value in grain and oil crops. Soybeans require more nitrogen, but can be fixed by root nodules, generally from the atmosphere to obtain 5 to 7.5 kg / mu, about soybean 40% to 60% of nitrogen. Every 100 kilograms of soybean produced requires 1.8 to 10.1 kilograms of nitrogen from the soil, 1.8 to 3 kilograms of phosphorus and 2.9 to 3 kilograms of potassium. Soybeans absorb much more nutrients than rice, wheat and corn.
Next Article
Check valve installation and use
Prev Article
Safety valve overview